
Your pricing may not recover the costs of items that are more expensive, which can lead to loss with your sales price.

Besides, accountants do not need to process the detailed records for each purchase – they need to process records only for the totals. Alternative methods require accountants to use a variety of costs, depending on individual costs incurred with each transaction. This includes the cost used for the ending inventory value and the cost of goods sold. After the product cost is calculated, that cost can be used for all inventory items. Consistency – With the weighted average method, the product cost of your inventory will be consistent.Smoothened price fluctuations – When prices fluctuate around an average, average costing method will help you be more confident that you are not underpricing.The average cost method allows such compliance, unlike LIFO, which reduces taxation figures and thus can lead to problems with international tax authorities. Compliance with the International Financial Reporting Standards – If your business operates internationally, it needs to comply with the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).Cost efficiency – Due to its simplicity, the average costing method is also the most cost efficient method as it requires little input.You can just mark up the average price of the items. Saved time – When you pick inventory items, you do not have to track their original cost before pricing them.It can be calculated even without an inventory management system. Ease of use – A simple formula makes it quite easy to calculate the average cost.The average cost method has the following benefits: Weighted average costing simplifies the accounting for these types of items. Food and agriculture – Agricultural and food products are collected in large amounts, and it is difficult to differentiate them individually.Oil companies – Same as with manufacturers, batches of oil and petrol can be mixed, so the weighted average method is the best one here as it helps to avoid confusion between the items within a batch.The average cost method makes it easier to account for such items. As a result, it becomes difficult to distinguish between the older and the newer items in the same batch. Manufacturers (clothes, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, etc) – Inventories of manufacturers often involve mixed batches of the same product.The average costing inventory method is typically used in the following sectors: Long-term planning – If you use average cost for long-term purposes, such as budget planning, then the weighted average method will be helpful in case of raw material cost fluctuations.Identical inventory items – If you have large volumes of identical items that are moving fast through your inventory system, you can use the weighted average method to save time on tracking each item individually.It’s suitable for the following situations: Wondering when to apply the weighted average method? Therefore, $11 is the average cost for this item. This means that the cost of all 15 pairs is treated as if they were $11 each.
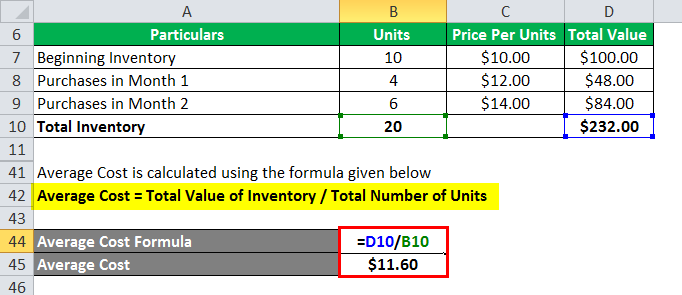
Five of them cost $10 per unit, the next five cost $ 11 per unit and the remaining five cost $ 12 per unit. To calculate average cost, take the cost of goods available for sale and divide it by the total number of items from the beginning inventory and purchases.įor example, a clothing store has 15 identical pairs of jeans in stock. The average cost calculation formula is as follows:
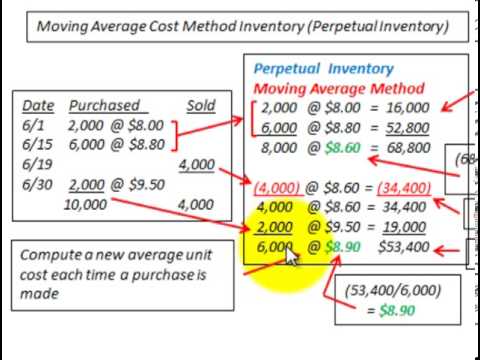
In this article, we are going to explain the average cost inventory calculation in more detail as well as highlight the pros and cons of this method. The average cost method is an alternative to FIFO or LIFO, which use the actual prices paid for each unit, even if the costs change. Average costing assigns all inventory items a single cost price derived from the average cost of all those items. The cost of goods sold, or COGS, includes both the costs of the inventory items and additional expenses, such as shipping costs, customs fees and packaging. Average cost method, or weighted average, is one of the inventory valuation methods that help to calculate the cost of goods sold.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
